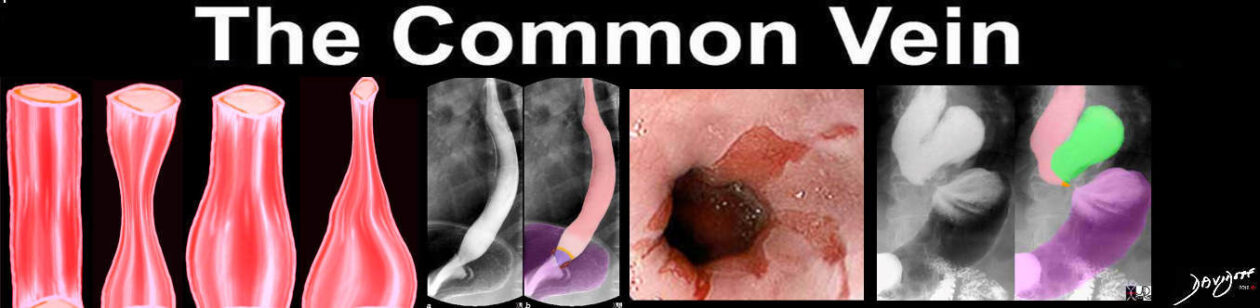
Stages of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus
The stages for adenocarcinoma of the esophagus include:
Stage 0 (high-grade dysplasia)
Abnormal cells that may become cancer develop in the mucosa.
Stage I
Stage I has 3 sub-stages:
- Stage IA: Low grade (slow-growing) cancer in the mucosa but no spread to surrounding tissue
- Stage IB: Low or higher grade (faster-growing) cancer in the mucosa or submucosa but no spread to surrounding tissue
- Stage IC: A higher grade cancer in the mucosa or submucosa or a low grade cancer in the muscularis propria, but no spread to lymph nodes or distant organs.
Stage II
Stage II sub-stages include:
- Stage IIA: Higher grade (fast-growing) cancer cells that have spread into the muscularis propria, but no spread to tissue beyond this area.
- Stage IIB: The cancer has either of these features:
- Cancer has spread into the adventitia, but has not spread to lymph nodes or other organs.
- Cancer in the mucosa or submucosa and cancer in 1 or 2 nearby lymph nodes
Stage III
There are 2 sub-stages in stage III:
- Stage IIIA:
- Cancer in the mucosa or submucosa and 3 to no more than 6 nearby lymph nodes
- Cancer in the muscularis propria with spread to 1 or 2 nearby lymph nodes
- Stage IIIB:
- Cancer in the muscularis propria and spread to 3 but no more than 6 nearby lymph nodes.
- Cancer in the adventitia and no more than 6 nearby lymph nodes
- Cancer in the muscle that divides your chest and abdomen (diaphragm), the sac that encases the heart (pericardium), or the tissue that lines the chest cavity (pleura) and no more than 2 nearby lymph nodes
Stage IV
There are 2 sub-stages in stage IV
- Stage IVA: The cancer has any of these features:
- Cancer in the pleura, diaphragm, or sac that encases the heart, as well as 3 to 6 nearby lymph nodes
- Cancer has spread to nearby organs such as the trachea or spine
- Cancer has spread to 7 or more nearby lymph nodes
- Stage IVB: Cancer has spread outside the esophagus to other areas of the body.
Recurrent: Cancer that has come back after treatment. This may be managed by some combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.